Factors that Increase the Risk of Prostate Cancer
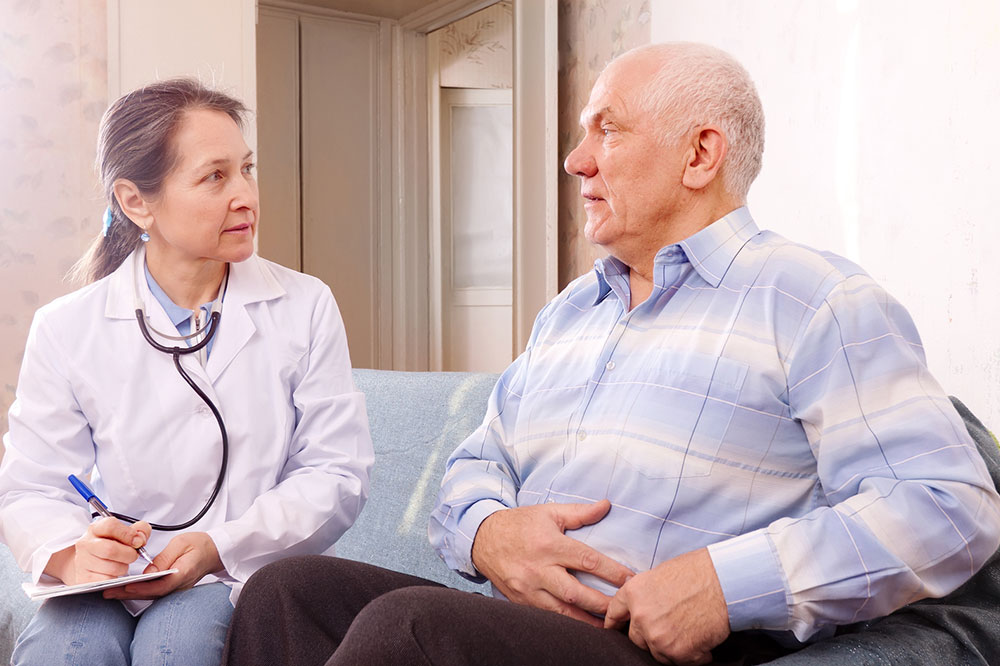
The prostate gland in men has an important function of producing the seminal fluid that transports and nourishes sperm. Cancer in the prostate gland is one of the common types of cancer affecting men, and it can also spread to other parts of the body if not treated early.
According to the CDC, 13 out of every 100 men in the country get prostate cancer, and 2 to 3 of them may die because of it.
This article looks at the top risk factors that increase the chances of a man developing prostate cancer. Anyone who is at risk of developing this condition needs to be careful and undergo tests to ensure that they can be diagnosed early and get timely treatment in case they develop this disease:
- Age
Prostate cancer usually affects men over the age of 50 years. Over 80% of cases of the disease are in men who are more than 65 years of age. It is very unlikely to affect younger men. - African ethnicity
Prostate cancer affects African-American men more than those belonging to other ethnicities. It is also found that when Afro-Americans or people of Caribbean descent get prostate cancer, it can affect them even at a younger age and be more severe and advanced. - Regional factors
The highest incidence of prostate cancer occurs in North America, the Caribbean islands, Australia, and Northwest Europe. Again, the reason for this is not very clear. - Family history
Another top risk factor for prostate cancer is the family history of an individual. Like in the case of most other diseases, those with a family history of prostate cancer are at a higher risk of being affected by it. If anyone in one’s family has this disease, they have a higher chance of getting it as well. Studies have shown that the risk is higher if a person has a brother with this form of cancer than the father. Additionally, the risk is higher if multiple relatives have had the disease, and especially if they were young when it was diagnosed. - Diet
Some studies have shown that those who eat red meat or high-fat foods may have a slightly higher risk of developing prostate cancer, but the role of this factor is not concrete in the development of the disease. - Obesity
One of the top risk factors for prostate cancer is being excessively overweight. Also, overweight men are more likely to have aggressive variants of cancer with a higher fatality rate. - Prostatitis
Inflammation of the prostate, or prostatitis, is a disease that may be linked to the risk of developing prostate cancer, but this is not yet clear. - Sexually transmitted infections
It is believed that sexually transmitted infections like gonorrhea can increase one’s risk of developing prostate cancer. - Gene mutations
Studies have shown that inherited mutations in the genes can be one of the top risk factors for prostate cancer.