Top Treatment Options for Spinal Muscle Atrophy
Spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) is a neurological disorder that is caused by a genetic condition. It is a motor neuron disease that causes a loss of nerve cells in the spinal cord and brain stem due to which the patient is not able to control their muscle movements. Since SMA causes muscle wasting and weakness it makes it difficult for the patient to not only walk and turn their heads but also to swallow and breathe. There is no cure but only treatment options that help to slow down the progress of spinal muscle atrophy.
SMA is usually diagnosed when the child has symptoms of muscle weakness and reduced muscle tone. It is confirmed through electromyography (EMG) tests, a creatine kinase (CPK) test and sometimes genetic testing. SMA is classified into different types based on the age at which the symptoms start to appear as well as the severity of the symptoms.
The top treatment options that help improve and manage the symptoms of spinal muscle atrophy are
Medication
There are two approved medications that are used in gene therapy to treat SMA: Nusinersen or Spinraza and Onasemnogene Abeparvovec-xioi or Zolgensma. Both these therapies target the SMN1 and SMN2 genes that are involved in the condition. These genes are responsible for the production of the protein that controls muscle movement. Studies have shown that in 4 out of 10 patients, it improves strength.
Nusinersen is used when the patient is suffering from SMA caused by the SMN1 gene mutation. It is injected into the fluid around the patient’s spinal cord. The treatment may require that repeated doses be administered. The medication targets the SMN2 gene and is suitable for adults and children with SMA. Studies have shown that this treatment helps some children sit and control their heads faster.
Breathing
The muscle weakness caused by SMA especially in types 1 and 2 can cause breathing issues. When this happens, breathing support may be provided by means of a mouthpiece, mask or machine depending on how severe the problem is.
Eating
Muscular weakness impacts the ability to suck and swallow. This makes it difficult for the child to take in enough nutrition. Patients will have to be managed by a nutritionist to ensure adequate nutrient intake. A feeding tube may be required for some babies.
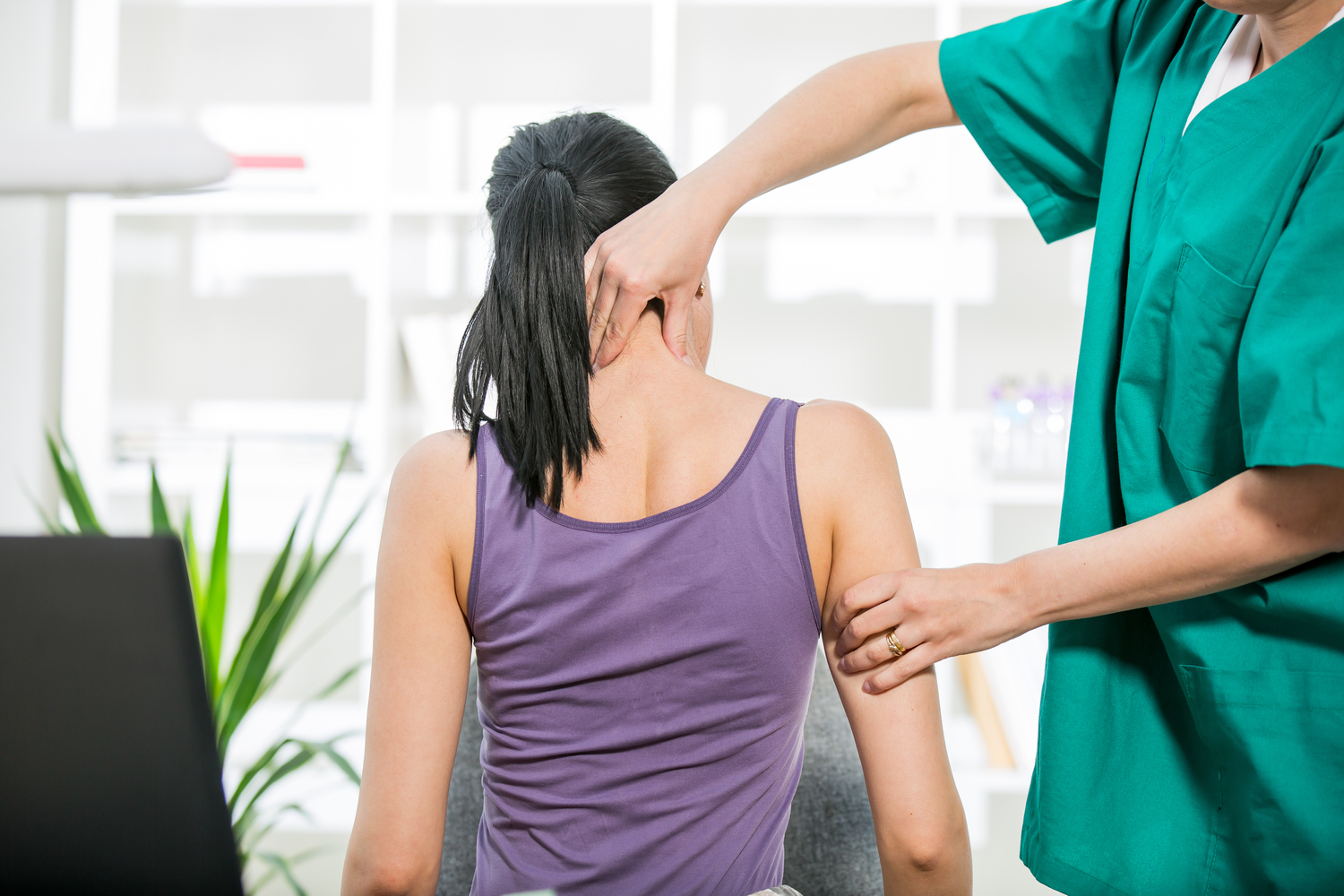
Movement
Physical therapy and supporting devices such as braces, walkers or an electric wheelchair may be used to support the patient. Regular physical therapy and exercise are essential.
Spinal Support
Patients who have had an onset of SMA in childhood have a curved spine. Using a back brace for spinal support may help prevent this during the growing years. Surgery to correct the spine may also be performed.
A patient of spinal muscle atrophy will have to have periodic checkups with specialists to detect issues and provide the appropriate treatment options. The usual checkups would include the lungs, bones, nerves and digestive system. Regular reviews of physical therapy and nutrition are very important.